**Summary of Bearing Heating Common Sense**
Bearing heating is one of the most common issues users encounter during the operation of machinery. Bearings are essential components that support rotating shafts and ensure smooth motion within a machine. If bearings fail or overheat, the entire system can be affected, leading to reduced efficiency, premature wear, or even complete failure.
Understanding the causes of bearing overheating is crucial for maintaining equipment performance and extending its lifespan. Here are some common reasons why bearings may overheat:
1. **Insufficient Lubrication**: When the oil level is too low, the lubricant may not adequately cover the bearing surfaces, leading to increased friction and heat generation.
2. **Overfilling with Grease**: Excessive grease in the bearing housing can cause excessive churning, which increases temperature and may result in oil leakage.
3. **Dry or Tight Seals**: If the contact seal (such as an oil seal) becomes dry or the spring is too tight, it can create unnecessary friction and heat.
4. **Misalignment or Poor Fit**: If the bearing housing is not round, deformed, or the inner diameter is incorrect, the bearing may not fit properly, causing uneven load distribution and overheating.
5. **Improper Installation**: Incorrect installation, such as using improper tools or applying excessive force, can damage the bearing and lead to abnormal heat.
Regular maintenance, proper lubrication, and correct installation are key to preventing bearing overheating. It’s also important to monitor the operating temperature of bearings and address any signs of abnormal heat promptly.
If you're looking for more information on bearings, check out our related articles on NTN bearing types, lubrication methods, and troubleshooting techniques.
For more details, visit [China Bearing Network](http://www.chinabearing.net).
Previous: Rolling Bearing English Translation
Next: Basic Knowledge of Bearing Fit
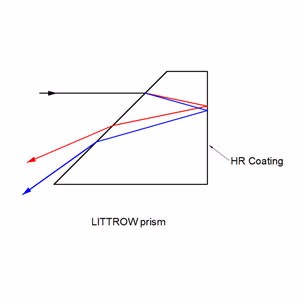
Dispersion Prism
Littrow prisms feature 30°, 60°, and 90° angles .30° - 60° - 90° Littrow Dispersion Prisms can be used for a variety of applications. Uncoated littrow dipersion prisms are used to disperse light into its component spectrum. Coated littrow dipersion prisms are used to deviate the line of sight by 60°.
Dispersion Prisms (Uncoated)
Collimated white light enters into the A-C surface of the prism, is reflected at the hypotenuse surface, and then dispersed into its component spectrum at the B-C surface. Although Littrow prisms produce narrower dispersion than equilateral prisms, Littrow prisms are typically less expensive.
Beam Deviation Prisms (Coated)
Incident light enters into the aluminum coated B-C surface of the prism at the nominal angle and returns back using the same path. In spectrum dispersion applications utilizing white light, the resolution performance of Littrow prisms is equal to equilateral prisms since the optical path length through the glass substrate is the same distance round-trip. Additionally, light entered into the A-C surface will reflect twice inside the glass substrate before being emitted through the hypotenuse surface at 60°.
Â
Dispersion Prism,Optical Dispersion Prisms,Beam Deviation Prisms,Inked Dispersion Prism
China Star Optics Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.csoptlens.com
