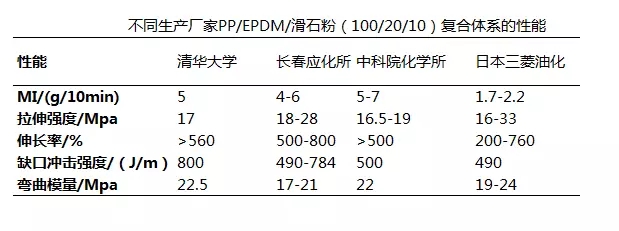
(1) PP/PE toughening system (2) PP/EVA toughening system EVA can also increase the elongation at break, melt flow index and surface gloss while toughening PP. The VA content of the selected EVA is between 14% and 18%. Toughening PP with 20% EVA-15 has a 12-fold increase in impact strength, a small decrease in rigidity, and a lower cost than elastomer or rubber toughened PP. The overall performance is better than that of PP/EPDM system. (3) PP/PA6 toughening system PP/PA6 blending system can improve the inherent disadvantages of the two, so that the material has excellent comprehensive performance index. When 15% PA6 is added into PP, the impact strength can be increased by 50% and the tensile strength can be decreased by 13.8%. 5% PP-g-MAH as a compatibilizer can increase the impact strength by 113% and the tensile strength by 2.7%. (4) mPE/PP toughening system mPE has a very low glass transition temperature and a large elongation at break, which is very suitable for toughening modification of PP. mPE has a better toughening effect on PP. 40% mPE is added to PP, and the notched impact strength at -30 °C is 20 times higher than that of pure PP, which is about 9 times that of equivalent mass fraction EPDM. It has also been found that toughened PP with mPE, the composite has low tensile set, compression set and creep deformation, excellent low temperature performance and processing performance, and has become a strong competitor of EPDM. In addition, the newly developed toughening material is ethylene-octene copolymer EOC, which can increase the impact strength of PP by 9 times. (5) POE toughened PP system PP/POE is an elastomer-toughened PP system developed in recent years. It has the best toughening effect, good weather resistance, good fluidity, good thermal stability and good processing performance. It is also the most commonly used elastomer toughened PP system. . The compatibility between POE and PP is very good. The toughening effect, especially the low temperature toughening effect, is very obvious. It is better than EPDM and EPR. The toughening effect is POE>EPDM>EPR, and the bending modulus and tensile strength decrease are small. , the descending order is POE When the amount of POE added in the PP exceeds 15%, the toughening effect is rapidly increased. When 30% POE was added to PP, the notched impact strength increased from 76.4 J/m of pure PP to 626 J/m. Compared with EPDM, POE has low cohesive energy, no double bond and good weather resistance, and is a powerful substitute for EPDM. (6) SBS toughened PP system SBS has a toughening effect on PP that is not as good as EPDM, but can be used in general applications. Studies have shown that when the content of SBS is between 0 and 10 parts, the impact strength increases with the addition amount; after more than 15 parts, the impact strength decreases. The normal temperature and low temperature impact properties of the impact resistant PP made of SBS and PP can be increased by 5 times and 10 times, respectively. When the specific formula is PP:SBS:CaCO3=48:40:12, the impact strength of the cantilever beam is 70kj/m2. (7) EPDM, EPR toughened PP system EPDM (ethylene-propylene-diene terpolymer) and EPR (ethylene-propylene binary copolymer) are the most commonly used elastomer toughening materials for PP, especially EPDM, which have high elasticity and good resistance. Low temperature performance improves PP impact resistance and low temperature resistance. Since both structures contain a propyl group, compatibility with PP is good and thermal stability is very high. In the range of 5%-30%, the impact strength of the system increases linearly with the increase of the amount of addition; at the same time, the bending strength, tensile strength and heat distortion temperature of the system are significantly reduced. Compared with EPR, EPDM has good interfacial interaction with PP, and the solubility parameters are equal (all 8.1). The compatibility with PP is better, and the toughening effect on PP is more obvious. Taking EPR as an example, when 20% is added to PP, the normal temperature notched impact strength is increased by 10 times, and the embrittlement temperature is decreased by 4 times. Taking EPDM as an example, when PP/EPDM/talc powder is used in the ratio of 100/20/10 for automobile bumpers, the performance of different manufacturers is shown in the following table. After EPDM was grafted with MADM to form EPDM-g-MAH, the toughening PP with EPDM-g-MAH was better than pure EPDM. (8)BR toughened PP system Butadiene rubber (BR) has the advantages of high elasticity, good low temperature performance (glass transition temperature -110 ° C), wear resistance, flex resistance, etc. The solubility parameter of BR is close to that of PP, and the compatibility with PP is good. The toughening effect is good. When the PP/BR is 100/15, the impact strength is increased by nearly 6 times, and the embrittlement temperature is lowered to 8 ° C (down 23 ° C). (9) Plastic/elastomer synergistic toughening PP system Although the elastomer and PP blend have excellent impact strength, the performance loss such as rigidity, strength and heat distortion temperature is large, and the cost is obviously improved. In order to improve the mechanical properties and reduce the cost, in the elastomer/PP toughening system, plastic is added to form an elastomer/plastic/PP ternary blend system. The most commonly used plastics in ternary blends are HDPE and LLDPE, specific examples such as PP/SBS/HDPE, PP/EPR/HDPE, PP/EPDM/LLDPE, PP/HDPE/BR (100/15/15), PP/PS/mPE, PP/PS/SBS, etc. PP/HDPE/BR ternary toughening system, when the ratio is 100/15/15, not only has good toughness, but also has high tensile strength and flexural strength. The synergistic effect of the PP/SBS/BR ternary blend system is significant, and the toughening effect is much better than that of a single PP/SBS or PP/BR. The following points should be noted for the formulation design of the above toughening system. 1 toughening effect. POE>mPE>TPE>EPDM, but more economical considerations use EPDM. 2 choice of compatibilizer. For toughening materials with poor compatibility with PP, compatibilizer should be added in the formulation design, commonly used PP-g-MAH. After the addition of the compatibilizer, the impact strength increases significantly. For example, PA, PS, PVC, etc., need to add a compatibilizer. 3 Determination of the amount added. Various toughening materials have an optimum range of toughening effect on PP. For example, SBS has a good effect below 15%, and POE is better than 15%. 4 selection of toughening materials. The toughening effect of different toughening materials has different effects on other properties, so the performance requirements of PP for different applications are also different. The toughening materials should be selected according to the specific properties. For example, EPR toughened PP has poor aging resistance, and automotive bumpers for outdoor use generally do not select EPR and select EPDM with better weather resistance. 5 composite toughening. A single material toughened PP, although the impact strength is improved, but has a greater impact on other properties. For this reason, composite toughening is often used to balance performance in all aspects and to reduce costs appropriately. 6 The particle size of the elastomer. When the particle diameter is less than 1.5 μm, a better toughening effect can be obtained. (10) Inorganic rigid particle toughened PP system Commonly used inorganic rigid toughening materials are mica, talc, wollastonite, calcium carbonate and barium sulfate. The pre-toughening system is made of rubber, and after the appropriate surface treatment of the inorganic rigid particles, a core-shell dispersion structure in which inorganic rigid particles are used as a core and rubber as a shell can be formed, and the toughening effect of the inorganic rigid particles is remarkable. Specific application examples are PP/EPDM/CaCO3, PP/EPDM/talc, PP/EPDM/wollastonite, and the like. The rubber-free pre-toughening system has a large treatment intensity for the inorganic rigid particles, and it is preferable to add a coupling aid at the same time as the coupling agent is added, and the composite treatment effect is good. For the inorganic rigid particles optimized by the interfacial modifier, a shell-shell dispersion structure in which inorganic rigid particles are used as a core and an interface modifier is used as a shell can also be formed. For example, PP/optimized kaolin toughening system, when kaolin is added to 30%, the impact strength is as high as 480 J/m; for example, when CaCO3 treated with alkyl carboxylate and co-coupling agent is added to 50% of PP The impact strength can be increased by about 1 time. (11) Toughening of organic/inorganic nanomaterials Nanomaterials are new materials that have just been developed in the 1980s. They are also the most promising new materials in the 21st century. They are widely concerned. Inorganic nanoparticles have few surface defects, many unpaired atoms, and large specific surface area. The effect can improve the crystallization behavior, crystal structure and mechanical behavior of PP in the interface region, so as to achieve the purpose of strengthening and toughening. Volleyball Plastic Grass, Volleyball Grass, China Volleyball Plastic Grass JIANGSU WMGRASS CO., LTD. , https://www.wmgrassturf.com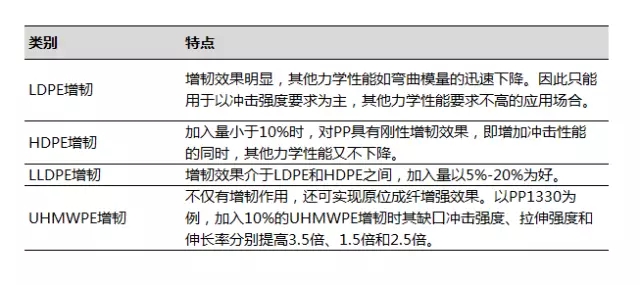

/*kangxianyue 250*250 was created on 2017/3/29*/ var cpro_id = "u2939694";